Report: China's fight against COVID-19 (full text)
I. Universal consensus and public mobilization
To deal with such a pandemic, it is essential to fully understand the situation and mobilize the general public to do whatever is required of them.
On the one hand, Chinese authorities released timely data in an open, transparent and responsible manner to provide people with dynamic, clear and important information so that they could fully understand the government's policies, strategies and measures to deal with the epidemic. Making sure "the public is fully informed" is key to establishing strong social consensus.
On the other hand, with a strong sense of social responsibility and trust in the government, people actively participated in the nationwide fight against the virus: a "people's war" powered by a united will. Relying strongly on people is a key component in "winning the war".
1. Timely release of information

— A daily news release mechanism was established to publish vital information. In the two months after the outbreak, the Information Office of the State Council, Hubei province, the hardest hit area in the country, and other departments held nearly 200 press conferences; other provinces and municipalities have also done the same. The live broadcasts updated the public with the latest developments and addressed public concerns at home and abroad.
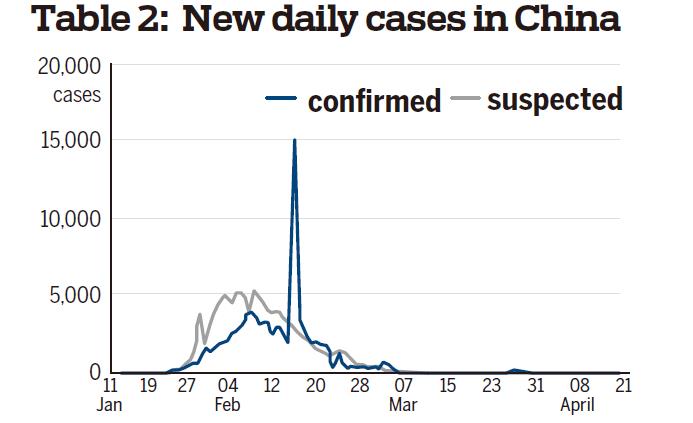
— A daily report system was launched to provide accurate and comprehensive data. The National Health Commission announced on its websites and other platforms the numbers of new confirmed, suspected, recovered, discharged cases and deaths, the number of people who have had close contact with confirmed cases and under medical observation, and the updated number of asymptomatic cases, as well as similar data in Hong Kong, Macao and Taiwan.

— The revision of COVID-19 statistics was made in accordance with law. In the early stages of the outbreak, due to unverified deaths at home as a result of the lack of hospital capacity and incomplete registration, there were late, repetitive, erroneous and missing reports.
After the outbreak was basically brought under control, Wuhan organized an epidemiological investigation with the help of big data technology and based on that, the city revised the numbers of confirmed cases and deaths. The number of deaths added was 1,290, bringing the total number to 3,869 in the city.
— The "epidemic map" was updated in real time to display figures on infections and deaths. All regions could refer to the map, which is supported by big data technology, for the precise location and number of infection cases in a specific community to respond in quick time and promptly formulate traffic control and other measures.
2. Dissemination of knowledge about prevention and control
— Key opinion leaders played a major role in raising public awareness of scientific prevention and control. Scientists and research institutions regularly released professional opinions and suggestions via press conferences, interviews and the internet and widely promoted simple but effective self-protection measures such as wearing face masks, washing hands regularly and ventilating rooms.
— Practical and feasible prevention and control guidelines were also issued. The National Health Commission published six public prevention guidelines for general occasions, travel, family, public places, public transport and medical observation at home, as well as a question-and-answer manual specifically for rural residents. The Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention published a "Guideline for Public Prevention of Pneumonia caused by Novel Coronavirus" which helped the public understand prevention methods and answered their questions about individual and family preventive measures, medical observation at home, medical treatment and psychological counseling.
— Psychological intervention was also used to guide the public to get through the trying times. The National Health Commission issued "Guiding Principles for Emergency Psychological Intervention for Pneumonia caused by the Novel Coronavirus" and a notice on psychological assistance requiring all localities to establish a hotline specifically to offer psychological help. Universities, online hospitals and related companies also opened psychological support hotlines and online counseling services.
3. Public opinion guidance and support by mainstream media
— The news media gave full publicity to the government's major policies and decisions. The mainstream media reported on the achievements in the fight against the virus and updated the public on what was to be done. They covered moving stories of frontline medical workers, community workers, volunteers, police officers and other officials. These stories inspired an increasing number of citizens from all walks of life to participate in prevention and control efforts across the country.
— Mass communication and digital media used their strengths to allay people's anxiety and fear. In addition to releasing a large amount of authoritative information on multiple channels, they also revealed existing problems, helped find solutions and answered major public concerns in terms of anti-epidemic work, logistic support, development of vaccines and public donations. Many set up special columns on their platforms to interpret the situation, analyze data and research, predict trends and promptly debunk rumors with credible facts and detailed data.
4. Universal participation with social cohesion
— The people's active response to the government's call and their cooperation resulted in the entire society participating in efforts by government organs and social organizations. With solidarity and the experience of fighting the severe acute respiratory syndrome, or SARS, in 2003, government institutions, enterprises, social organizations, communities, volunteer groups, families and individuals all united as one.
— Citizens' self-discipline and their willingness to sacrifice facilitated the smooth implementation of prevention and control measures. Be it lockdowns of key areas, tight management of communities, home isolation or self-quarantine, family and personal hygiene habits or social distancing requirements, people laid a solid foundation for effectively reducing the rate of infection.
— Community-based management has been a key factor for curbing the spread of the virus. As an extension of governance for social management, 4 million community workers, together with volunteers, visited 650,000 urban and rural communities across the country to communicate epidemic prevention knowledge, offered psychological counseling and helped households receive daily necessities. They helped provide dragnet screening of potential virus carriers, made sure every corner was disinfected and helped millions of households with difficulties in making a living.
Please feel free to contact us by sending your questions to question@chinadaily.com.cn or commenting on China Daily app. We will ask experts to answer them.