How to improve the timeliness of nucleic acid testing?
It is important to note that the information provided in this Series is intended for your general knowledge only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice or treatment.
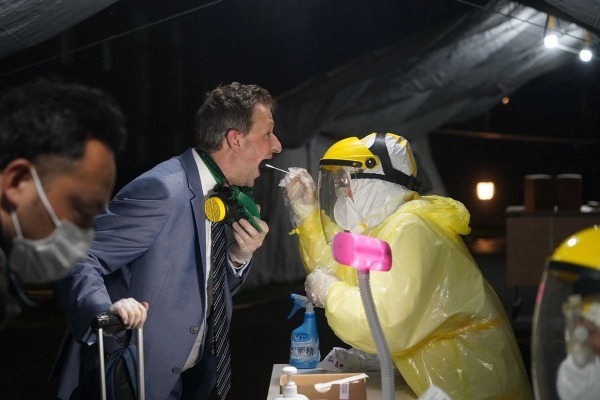

Nucleic acid testing is the primary method for diagnosing COVID-19. With strong specificity and relatively high sensitivity, it directly detects viral nucleic acid in collected samples. Early detection and quarantine of confirmed cases and treatment of those in need are all made possible because of nucleic acid testing. It is proved that the earlier nucleic acid test results come out, the earlier the patients can receive treatment, and the better it is for disease prevention and control.
There are 5 steps in nucleic acid testing: sample collection, transportation, nucleic acid extraction, PCR amplification and detection, and report. During the early stages of the outbreak, only disease control and prevention centers could carry out nucleic acid tests. The samples were collected by local centers then sent to the National Center for Disease Control and Prevention (National CDC) for verification. The entire process would take at least 2 days. Currently, due to the delegation of authority, the process only takes 6-8 hours.
With the increasing demand of testing, the Chinese government has delegated the power of collecting samples to medical institutions and the power of conducting tests from the National CDC to provincial and municipal CDCs, 3AAA hospitals as well as professional testing institutions. This decision not only expands the number of testing institutions, but also saves time on transporting samples to the testing institutions.
It should be noted, though, that there are prerequisites for the delegation of authorities. Delegating the power of collecting samples to medical institutions means that health care workers are facing bigger risks. As such, they need to be able to adequately protect themselves. Delegating the power of conducting tests requires every testing institution to have a Biological Safety Level 2 (BSL-2) laboratory and can conduct reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR).
Author: Hua Ruoyun, Center for International Knowledge on Development
Please feel free to contact us by sending your questions to question@chinadaily.com.cn or commenting on China Daily app. We will ask experts to answer them.